If the odds ratio is interpreted as a relative risk it will always overstate any effect size the odds ratio is smaller than the relative risk for odds ratios of less than one, and bigger than the relative risk for odds ratios of greater than oneRisk difference This study addresses the measures of effect, that is, the measures that are used to compare the frequency of disease (or other outcome) between two groups The measures of effect are generally expressed as relative risks and odds ratios (OR) (relative measures of effect) or as risk differenceRisk Ratio vs Odds Ratio The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomes If IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/ (IE IN)

1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
Odds ratio vs relative risk youtube
Odds ratio vs relative risk youtube-The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocolRelative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows Several statistics can be calculated such as relative risk and risk difference, relevant in prospective studies, and




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
In a cohort study, particularly on the occasion of a logistic regression, we replace the relative risk by the odds ratio if the disease is rare (incidence less than 10%) We illustrated both relative risks and odds ratios using bar charts, then looked at the types of study for which each statistic is suited We demonstrated calculation of relative risks and odds ratios through analysis of tabled data from a recent published longitudinal study, using a 2 × 2 table and R, the opensource statistical programming languagePublished 02 July 08;
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)Let us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)
The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks is feasible if INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should findFor instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an odds ratioAtive risk reduction (RRR) The relative risk of a treatment is the ratio of risks of the treated group and the control group, also called the risk ratio The relative risk reduction is derived from the relative risk by subtracting it from one, which is the same as the ratio between the ARR and the risk in the control group




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Of Death According To Biomarkers Of Risk Download Scientific Diagram
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another groupThe quote surely just means to say that the odds ratio is a relative risk measure rather than an estimate of the relative risk, which as already point out is only approximately the case in cohort studies/randomized trials for very low proportions By relative risk measure I mean something that is given relative to some comparison group in a way that the absolute difference depends on theThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies
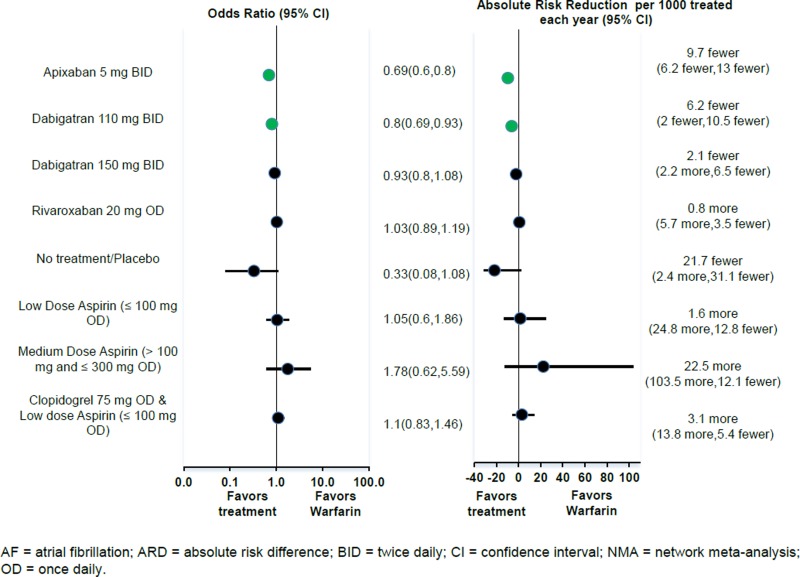



Figure 3 Odds Ratio And Absolute Risk Difference Of Major Bleeding For Antithrombotic Therapies Relative To Adjusted Dose Warfarin For Patients With Af Fixed Effects Nma Antithrombotic Agents For The Prevention Of Stroke




Bar Graph Represents The Summary Odds Ratios Or Relative Risks Of The Download Scientific Diagram
Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32 , 41 , 50 52




Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
Risk ratios At a minimum, the only change that needs to be done to get risk ratios is to change the link function that relates the mean value of the response variable to the linear predictor For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% =




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
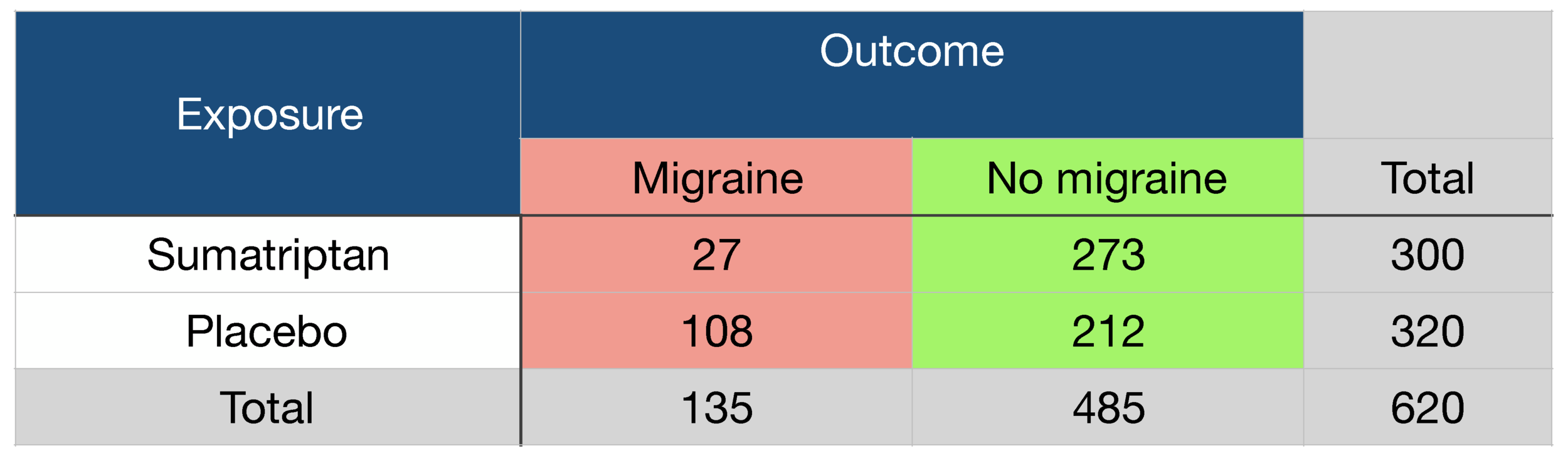



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj
The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskA risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal An example with a control group and a therapy treatment group Treatment group 5 deaths, 95 survive Risk = 5/100 = 005, Odds = 5/95 = 0053 Control group 8 deaths, 92 survive Risk = 8/100 = 008, OddsRelative risk is approximated by the odds ratio when the outcome of a particular result is uncommon (15% or less) With a common result, the two numbers diverge In logistic regression, the odds ratio equals the antilogarithm of a coefficient




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
When to use the odds ratio or the relative risk? For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions




Statistical Notes For Clinical Researchers Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 tableThe relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds ofSimilar to relative risk, the odds ratio for exposure is equal to a/c divided by b/d Similar to the odds ratio for exposure, the odds ratio for disease is equal to a/b divided by c/d, where a/b represents the odds for disease in those exposed to the risk and c/d represents the odds
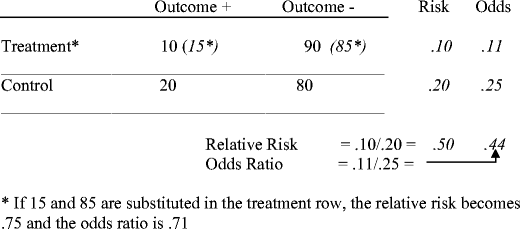



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithmFor example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31 Odds can be converted to risks, and risks to odds, using the formulae;For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Forest Plot Of Relative Risks Or Odds Ratios From Eighteen Download Scientific Diagram
Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with non For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including a Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents




Literature Search




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Abstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to useWhen to use the odds ratio or the relative risk?




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
Odds ratio and relative riskDownload PDF Download PDF Hints & Kinks;When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
Carsten Oliver Schmidt 1 & ThomasThe interpretation of an odds is more complicated than for a risk The simplest way to ensure that the interpretation is correct is to first convert the odds into a riskSee all my videos at https//wwwzstatisticscom/videos/Health Stats IQ playlisthttps//youtubecom/playlist?list=PLTNMv857s9WUI5YsQMW14trmbopjZMWPa000 Int



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo



Requesting Effect Measures




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Forest Plot Showing Relative Statistics Of Odds Ratio A And B Or Download Scientific Diagram



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Understanding The Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Simon 01 Journal Of Andrology Wiley Online Library




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Epidemiology Stepwards




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data




Math3010 Week 6




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Download Scientific Diagram



Q Tbn And9gcryvczzduvsmny9vwxy9g Twzvim6 Eyksppo1soy5c0lg1zri Usqp Cau
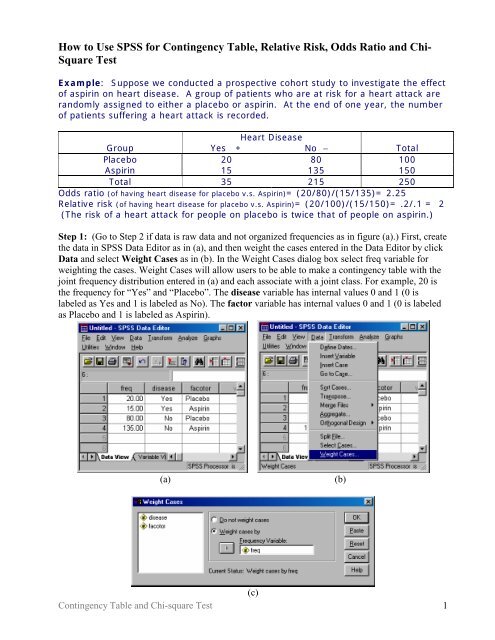



How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



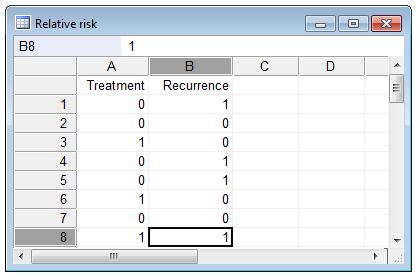
1




Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods
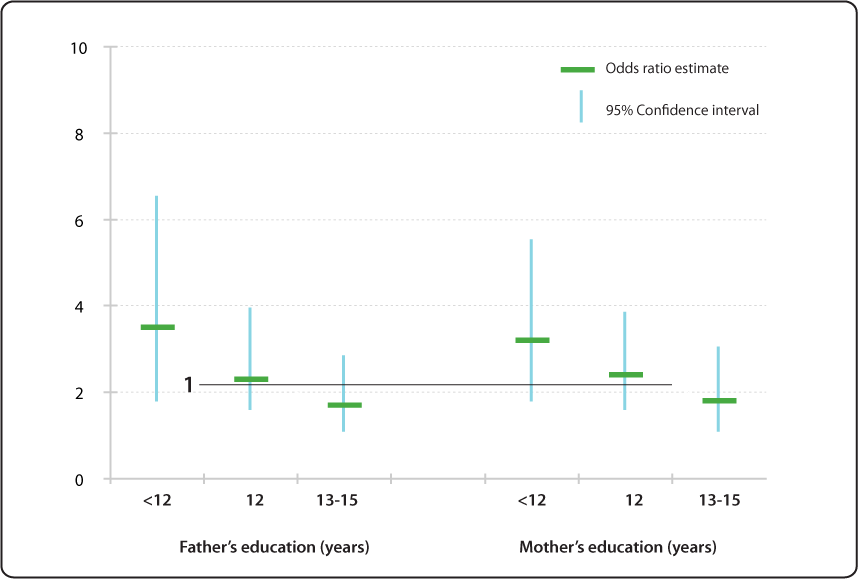



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau
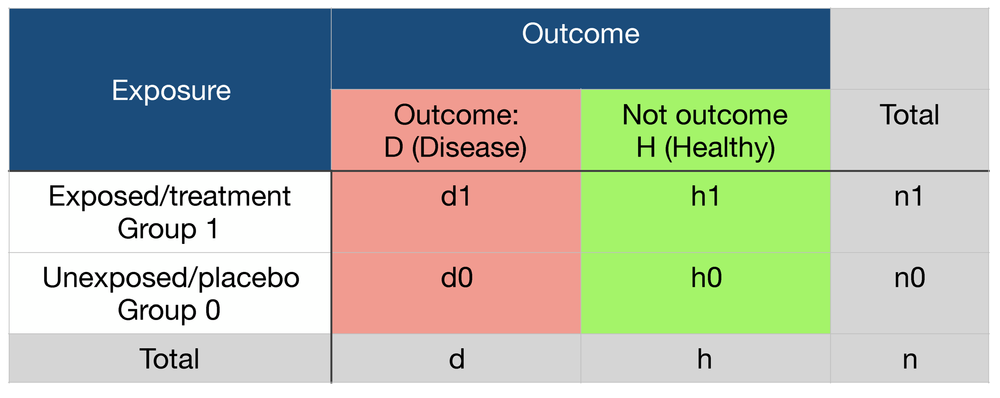



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect
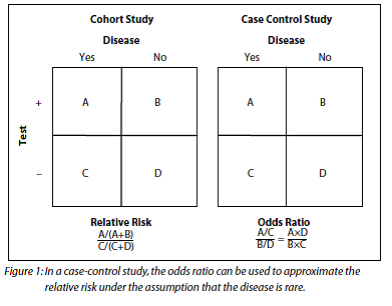



Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Health Informatics Statistics In Arabic Relative Risk Odds Ratio Youtube




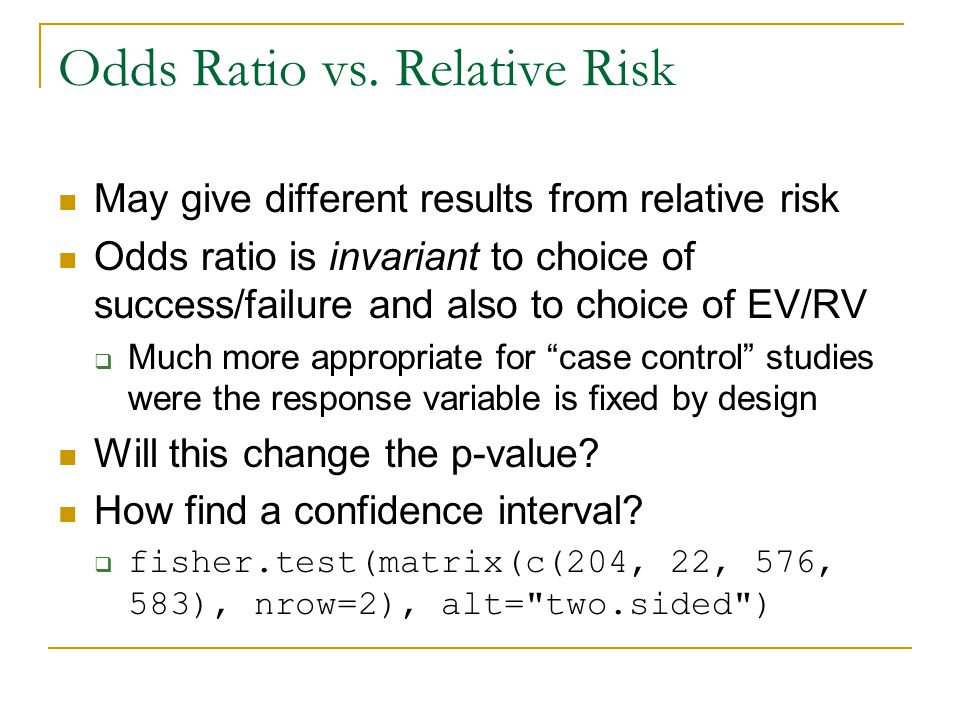
Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
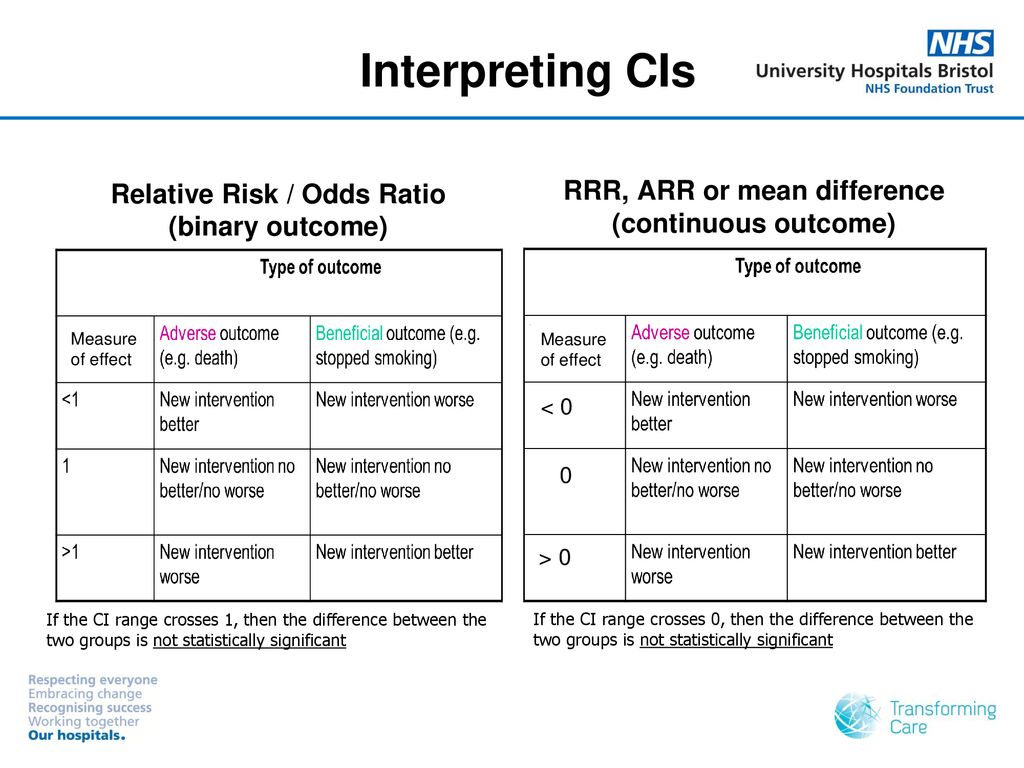



Interpreting Basic Statistics Ppt Download


